|
The previous blog post “Around the “Storage World” in no time – Storage vMotion for Oracle Workloads (RAC & Non-RAC) within same vSphere Cluster” addressed the following use cases of Storage vMotion of an Oracle RAC Cluster with shared vmdk(s) using multi-writer attribute . The following uses cases were addressed by the previous blog post for Oracle RAC clusters within the same vSphere Cluster – Migrate Oracle database storage from one Tier to another Tier within a storage array Migrate Oracle database storage from one array to another array (within and between data centers) for the same datastore type [ VMFS . NFS, iSCSI, vVOL, vSAN] Migrate Oracle database storage from one array to another array (within and between data centers) across different datastore types [ VMFS , NFS, iSCSI, vVOL, vSAN] For Customers deploying their Oracle RAC workloads on vSAN storage, the ask is to have the capability to migrate an Oracle RAC Cluster using shared disks using multi-writer attribute, ONLINE, without any downtime, from one vSAN Cluster to another vSAN Cluster within the same Virtual Center. Some of the advantages such a capability would bring to the table includes the ability to move from one vSAN Cluster to another vSAN cluster without any disruption in business SLA’s or downtime for hardware refresh reasons we still are faced with situations where we have stranded storage capacity in different vSAN clusters and we would like to use those stranded Storage capacities, yet continue to consume Compute from the current cluster One of the use cases that comes into mind is the high cost of Oracle Licensing. With such a capability, one could seamlessly and transparently move Oracle compute into smaller density (Physical sockets / cores) servers in a different vSAN cluster, thereby significantly reducing their Oracle Licensing costs move the Storage for Oracle workloads into a different vSAN cluster, if needed, where excess storage capacity is available
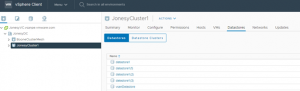
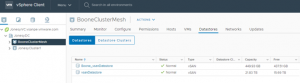
Who says you can’t have your cake and eat it too? Yes you can.. Drumroll…. Introducing VMware vSAN HCI Mesh technology in vSAN 7 Update 1. This blog demonstrates how we can achieve Storage vMotion of Oracle RAC Cluster using shared vmdk’s with multi-writer attribute ONLINE , with NO downtime, from one vSAN to another vSAN Cluster using VMware HCI Mesh VMware vSAN HCI MeshHCI Mesh is a unique, software-based approach for disaggregation of compute and storage resources. HCI Mesh brings together multiple independent vSAN clusters for a native, cross-cluster architecture that disaggregates resources and enables utilization of stranded capacity. Simply, vSAN allows one or more vSAN clusters to remotely mount datastores from other vSAN clusters (servers) within vCenter inventory. This approach maintains the essence and simplicity of HCI by not fundamentally changing the existing HCI model or requiring specialized hardware. Now, a cluster with excess compute can mount excess storage from a remote vSAN cluster. vMotion / HA / DRS are all officially supported for interoperation in this configuration Currently, at this time, the only limitation is, it is not supported to split VMDKs of a given VM across multiple datastores. So, recommendation is to disable HA for those VM’s during the storage migration process and then enable HA for the VM’s back. The current HA limitation is only applicable to VM spanning multiple vSAN datastores. For example, in the case of an Oracle RAC Cluster, the storage migration process includes both the steps More information on VMware vSAN HCI Mesh can be found here. Oracle RAC Disk modesOn a high level, there are 3 values of disk (vmdk) sharing mode in a VM Unspecified No sharing Multi-writer – used for Clustering Oracle RAC VM/s will have 2 genres of vmdk’s: non-database vmdk’s Operating System disks which house the root file system (/) Oracle binaries vmdk which houses the Oracle binaries (Grid and RDBMS binaries) (/u01) shared database vmdk(s) using multi-writer attribute Caveats with Multi-writer disks and Storage vMotionThe multi-writer capability for sharing vmdk’s between VM’s play an important role in Oracle RAC deployments on VMware SDDC. The multi-writer option allows VMFS-backed disks to be shared by multiple VM’s. This option can be used to disable the protection for certain cluster-aware applications e.g., Oracle Clusterware, where the applications ensure that writes originating from two or more different VM’s does not cause data loss and ensures data consistency and concurrency. Among the unsupported actions for shared vmdk’s using multi-writer capability includes Storage vMotion Snapshots Changed Block Tracking (CBT) Attempting a storage vMotion of an RAC VM will result in an error. The supported and unsupported actions / features using multi-writer attribute can be found in the KB 1034165. HCI Mesh Setup We have 2 vSphere Clusters with vSAN storage attached to the same Virtual Center. BooneClusterMesh with vSAN datastore ‘Boone_vsanDatastore’ JonesyCluster1 with vSAN datastore ‘vsanDatastore’
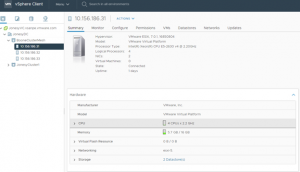
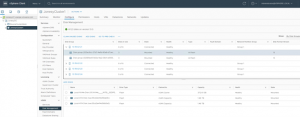
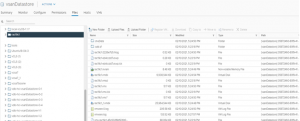
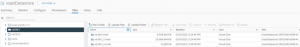
For this use case the source vSAN datastore is ‘Boone_vsanDatastore’ in vSphere Cluster ‘BooneClusterMesh’ target vSAN datastore is ‘vsanDatastore’ in vSphere cluster ‘JonesyCluster1 Source vSphere Cluster ‘BooneClusterMesh’ server details is shown below.
Source vSAN datastore ‘Boone_vsanDatastore’ disk group information is shown below
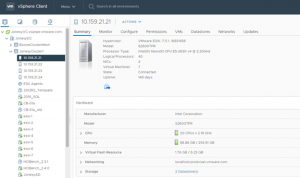
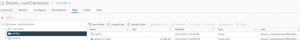
Target vSphere Cluster ‘JonesyCluster1’ server details is shown below.
Target vSAN datastore ‘vsanDatastore’ disk group information is shown below
Steps to set up VSAN HCI Mesh is shown here . More information on vSAN HCI Mesh can be found oin the VMware vSAN HCI Mesh Tech Note The vSAN HCI Mesh is shown below.
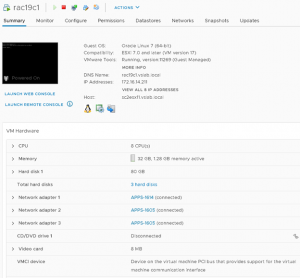
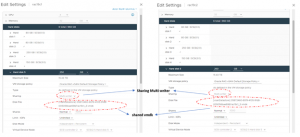
Oracle RAC Cluster ‘rac19c’ has 2 RAC VM’s – rac19c1 and rac19c2 RAC VM ‘rac19c1’ detail are shown below
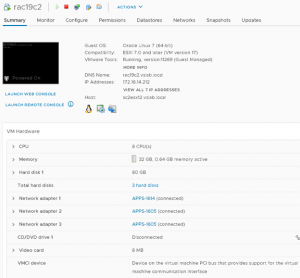
RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ detail are shown below
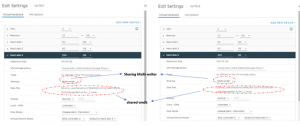
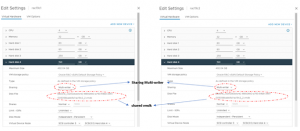
Both RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ have 4 vmdk’s Non-shared vmdk’s – Hard Disk 1 – 80 G Operating System Hard Disk 2 – 80 G Oracle Grid and RDBMS binaries Shared vmdk’s with multi-writer attribute – Hard Disk 3 – 250 G Oracle ASM DATA_DG Hard Disk 3 – 150 G Oracle ASM FRA_DG Oracle RAC Cluster ‘rac19c’ shared vmdk for DATA_DG is shown as below
Oracle RAC Cluster ‘rac19c’ shared vmdk for FRA_DG is shown as below
Recommendation is to have all vmdk’s created on one RAC VM with sharing set to Multi-writer and simply reference that vmdk as an ‘existing hard disk’ with sharing set to Multi-writer for other RAC VM’s. This use case deploys a RAC Cluster where the shared vmdk’s were created round robin among the RAC VM’s. The methodology / steps for Storage vMotion are the same for all implementations of Oracle RAC on vSAN, whether we round robin the shared vmdk’s among RAC VM’s OR create shared vmdk’s on RAC VM1 and reference the shared vmdk’s created on RAC VM1 on the remaining nodes of the RAC Cluster High level Steps
1. Disable HA for the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ VM’s during the RAC Cluster storage migration process. In the case of an Oracle RAC Cluster, the storage migration process includes both the steps Storage vMotion of non-shared disks from one vSAN storage to another vSAN storage Manual process of Oracle ASM add / rebalance process of the shared vmdk’s from one vSAN storage to another vSAN storage We can enable HA for the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ back. after RAC Cluster storage migration completes. 2. Perform Storage vMotion RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2 non-shared vmdk’s only to target vSAN without migrating the shared vmdk’s. 3. Add new shared vmdk’s with multi-writer attribute from target vSAN storage to RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2. Perform steps to add the new shared vmdk’s to the ASM disk groups DATA_DG and FRA_DG Drop the old ASM disks for DATA_DG & FRA_DG from Oracle ASM Then delete the old vmdk’s from RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2 Now the RAC database shared vmdk’s for DATA_DG & FRA_DG are on the target vSAN 4. Re-enable HA for the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ 5. As an optional step, perform Compute vMotion of RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2 ‘to target vSAN servers. As mentioned in the VMware vSAN HCI Mesh Tech Note , In an HCI Mesh Architecture, since VM’s living in one cluster may be using storage resources in another cluster, the network communication requirements will need to meet adequate levels of performance to not hinder the workloads. Latency between the clusters will add to the effective latency seen by the VMs using resources across a cluster. Test Steps1. Disable HA protection for the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ ‘rac19c2’ and during the RAC Cluster storage migration process.
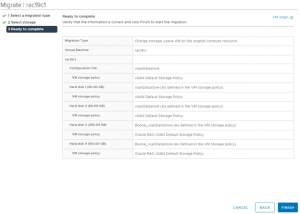
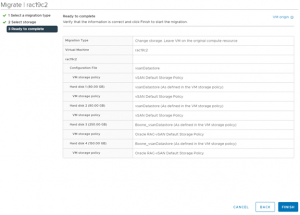
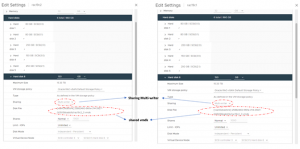
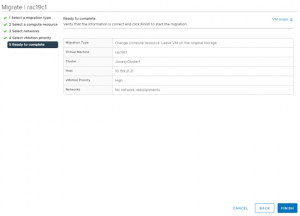
2. Perform Storage vMotion RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ non-shared vmdk’s only to target vSAN without migrating the shared vmdk’s. Choose ‘Change storage only’ option migration for non-shared vmdk’s. Choose the ‘Configure per disk’ option to select only the non-shared disk and the target vSAN datastore, leaving the shared vmdk’s to remain on the source vSAN storage.
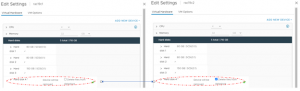
The details of the RAC VM ‘rac19c1’ non-shared vmdk’s Storage vMotion is shown as below, The RAC VM ‘rac19c1’ non-shared vmdk’s and configuration information is now successfully on the target vSAN storage.
The RAC VM ‘rac19c1’ shared vmdk is still on source vSAN storage.
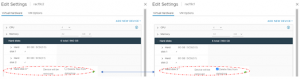
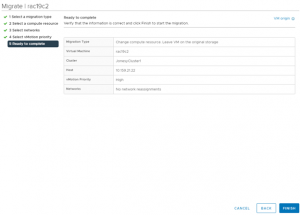
Migrate RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ non-shared vmdk’s to the target vSAN storage. The details of the RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ non-shared vmdk’s Storage vMotion is shown as below,
The RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ non-shared vmdk’s and configuration information is now successfully on the target vSAN storage.
The RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ shared vmdk is still on source vSAN storage.
3. Add new shared vmdk’s with multi-writer attribute from target vSAN storage to RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2. Perform steps to add the new shared vmdk’s to the ASM disk groups DATA_DG and FRA_DG. Drop the old ASM disks from Oracle ASM. Then delete the old vmdk’s from RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2. Now the RAC database (shared vmdk’s) is on the target vSAN. DATA_DG – Add new shared vmdk with multi-writer attribute (250G) from target vSAN at SCSI 2:1. on RAC VM ‘rac19c1’. Add the same disk to RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ as an existing disk on the same SCSI position.
We can see the shared disk ‘rac19c1_3.vmdk is now in the rac19c1’ folder on target vSAN.
FRA_DG – Add new shared vmdk with multi-writer attribute (150G) from target vSAN at SCSI 3:1. on RAC VM ‘rac19c1’. Add the same disk to RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ as an existing disk on the same SCSI position.
We can see the shared disk ‘rac19c2_3.vmdk is now in the rac19c2’ folder on target vSAN.
Perform steps to add the new shared vmdk’s to the ASM disk groups DATA_DG and FRA_DG. Drop the old ASM disks from Oracle ASM. SQL> alter diskgroup DATA_DG add disk ‘ORCL:DATA_DISK02’; SQL> alter diskgroup DATA_DG drop disk DATA_DISK01 rebalance power 11; SQL> alter diskgroup FRA_DG add disk ‘ORCL:FRA_DISK02’; SQL> alter diskgroup FRA_DG drop disk FRA_DISK01 rebalance power 11; You can run the below SQL statement to check the progress of the rebalance SQL>select * from v$asm_operation; Then delete the old vmdk’s from RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2.
At this point, the RAC database shared vmdk’s is on the target vSAN 4. Re-enable HA for the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ . Remove the VM override entries as shown below.
5. As an optional step, perform Compute vMotion of RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2 ‘to target vSAN servers. As mentioned in the VMware vSAN HCI Mesh Tech Note , In an HCI Mesh Architecture, since VM’s living in one cluster may be using storage resources in another cluster, the network communication requirements will need to meet adequate levels of performance to not hinder the workloads. Latency between the clusters will add to the effective latency seen by the VMs using resources across a cluster Compute vMotion details of RAC VM ‘rac19c1’ is shown below
Compute vMotion details of RAC VM ‘rac19c2’ is shown below
Final Result
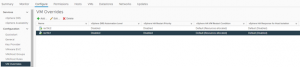
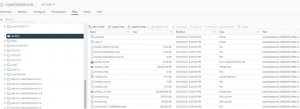
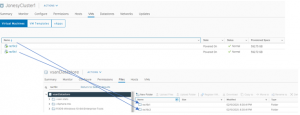
Both RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ are now in the new target vSphere cluster ‘JonesyCluster1’ with storage on vSAN datastore ‘vsanDatastore’
Checking source Sphere Cluster ‘BooneClusterMesh’ and vSAN datastore ‘Boone_vsanDatastore’ shows there are no RAC VM’s on the source datastore
Alternate Result In case we decide to leave the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ on the source vSAN cluster ‘BooneClusterMesh’ with vSAN datastore ‘Boone_vsanDatastore’ the RAC VM’s would consume Compute from source vSphere cluster ‘BooneClusterMesh’ the RAC VM’s would consume Storage from target vSphere ‘JonesyCluster1’ with vSAN datastore ‘vsanDatastore’
To reiterate, vSAN HCI Mesh is truly a is a unique, software-based approach for disaggregation of compute and storage resources. SummaryHCI Mesh is a unique, software-based approach for disaggregation of compute and storage resources. HCI Mesh brings together multiple independent vSAN clusters for a native, cross-cluster architecture that disaggregates resources and enables utilization of stranded capacity The following steps can be performed to achieve ONLINE without any downtime, Storage vMotion and Compute vMotion (Optional) of an Oracle RAC Cluster from one vSAN cluster to another vSAN cluster using VMware HCI Mesh technology. The high-level steps would be Disable HA for the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ VM’s during the RAC Cluster storage migration process. Perform Storage vMotion RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2 non-shared vmdk’s only to target vSAN without migrating the shared vmdk’s. Perform Oracle ASM Add/ Rebalance for new shared vmdk’s from target vSAN storage Re-enable HA for the RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2’ As an optional step, perform Compute vMotion of RAC VM’s ‘rac19c1’ and ‘rac19c2 ‘to target vSAN servers. Thanks to David Boone, Matt Jones, Peng Dai, Kristopher Groh for their valuable help in the review and content effort. (责任编辑:) |